Sachin Lalar and Arun Kumar Yadav
Department of Computer Science and Applications Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra
corresponding author email:sachin509@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojcst/10.01.23
Article Publishing History
Article Received on : March 09, 2017
Article Accepted on : March 16, 2017
Article Published : 22 Mar 2017
Article Metrics
ABSTRACT:
Routing protocol is the essential and vital performance factor in the Mobile Ad-hoc Network. The routing protocols in MANET are accomplished to handle a lot number of nodes with restricted resources. There is a variety of routing protocol exist in MANET. The routing protocol which is chosen may have an effect on the performance of network. In this paper, We perform a comparative study of DSDV, CSGR, WRP, AODV, OLSR, DSR, TORA, ZRP, ZHLS, DYMO routing protocol with respect to Routing Approaches, Routing structure, Route selection, Route, Routing table, Route maintenance, Operation of protocols, Strength, Weakness.
KEYWORDS:
MANET;Routing Protocol;DSDV; CSGR; WRP;AODV;OLSR; DSR;TORA;ZRP;ZHLS;DYMO
Copy the following to cite this article:
Lalar S, Yadav A. K. Comparative Study of Routing Protocols in MANET. Orient.J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;10(1)
|
Introduction
MANET (Mobile Ad hoc Network) is collection of mobile nodes which having the Autonomous Self -configuring network.In MANET, the nodes can flow freely and at any time it can connect to different nodes. Mobile nodes having the bandwidth restricted,dynamic topologies, Energy limited operation, variable infrastructure & capacity links. Routing protocol performs an essential function in any network [1]. Routing protocol specifies the routes between the nodes and disseminating information whichchoosethe routes between any two nodes on a network.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. The classifications of routing protocol in MANET are explained in section II. Further the comparisons of routing protocols DSDV, DSR, AODV & OLSR are explained in Section III. Concluding remarks are given in section IV.
Classification of Routing Protocol
There are different routing protocols existing in MANET. Routing protocols can be classified into three types: Proactive, Reactive routing protocol and Hybrid protocols. The routing protocols in MANET are accomplished to handle a lot number of nodes with restricted resources. The major concern in routing protocol is disappearing/ appearing of the nodes in various places. It is important to reduce routing message overhead despite the growing number of mobile nodes. Another important concern is to maintain the size of routing table small because if the size of routing protocol is larger than it can affect the control packet transferred inside the network.
Routing protocol is categorized on the idea of how and at what time route are discovered, however both pick the shortest path to the destination.
Proactive Routing Protocols
This type of routing protocols uses link-state routing algorithms which floods link information about its neighbours frequently. Proactive routing protocol stores the routing information and maintains the information up to date by exchanging the control packet from their neighbours. The examples of proactive routing protocols are DSDV, OLSR, and WRP etc [8].
Reactive Routing Protocols
Reactive routing protocols reduce overheads that are present in proactive protocols. It uses distance-vector routing algorithm and establishes the route to given destination only when a node request it by initiating route discovery process. There are number of reactive routing protocols available in MANET [4] like DSR, AODV, TORA and LMR etc.
Hybrid Routing Protocols
It is the mixture of reactive and proactive routing protocols. The example of Hybrid routing protocols are ZRP, BGP, EIGRP. Table 1 show the difference between the Proactive, Reactive routing protocol and Hybrid protocols in different features.
Table 1: Comparison between protocols [2]
|
Features
|
Reactive
|
Proactive
|
Hybrid
|
|
Routing Structure
|
Mostly Flat
|
Both Flat & Hierarchical
|
Hierarchical
|
|
Route Acquisition
|
On demand
|
Table driven
|
Combination of both
|
|
Routing Overhead
|
Low
|
High
|
Medium
|
|
Latency
|
High due to flooding
|
Low due to routing tables
|
Inside zone
Low outside similar to reactive protocols
|
|
Scalability
|
Not suitable for large networks
|
Low
|
Designed for large networks
|
|
Routing information
|
Available when required
|
Always available
|
Combination of both
|
|
Periodic Updates
|
Not needed
|
Yes whenever the topology of the network changes
|
Yes
|
|
Mobility
|
Route Maintenance
|
Periodic updates
|
Combination of both
|
|
Storage Requirement
|
Low
|
High
|
Medium
|
|
Bandwidth Requirement
|
Low
|
High
|
Medium
|
|
Power Requirement
|
Low
|
High
|
Medium
|
The figure 1 shows the example of the type of routing protocol.
Comparsion of Routing Protocol
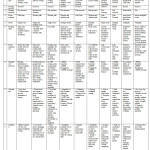
In this section, we will make the comparison of explain the ten routing protocol DSDV, CSGR, WRP, AODV, OLSR, DSR, TORA, ZRP, ZHLS, DYMO. The comparison is done with respect to Protocol type, Routing Approaches, Routing structure, Route selection, Route, Routing table, Route maintenance, Operation of protocols, Advantages, Limitation as shown in Table 2 [5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14].
Conclusion
This paper presents a comparative study of routing protocols in mobile ad-hoc networks. These protocols are divided into three: proactive or table-driven, reactive or on-demand, and Hybrid routing protocols. For each of these classes, we have reviewed several representative protocols. Each routing protocol has unique features. The main factor that distinguishes the protocols is the method of determining routes within source destination pairs. The routing protocol DSDV, CSGR, WRP, AODV, OLSR, DSR, TORA, ZRP, ZHLS, DYMO is compared with respect to Protocol type, Routing Approaches, Routing structure, Route selection, Route, Routing table, Route maintenance, Operation of protocols, Advantages, Limitation.
References
- Singh, G. and Singh, A. (2012) Performance Evaluation of Aodv and Dsr Routing Protocols for Vbr Traffic for 150 Nodes in MANETs. International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline. com), 2, 1583-1587.
- Kaur, R. and Rai, M.K. (2012) A Novel Review on Routing Protocols in MANETs. Undergraduate Academic Research Journal (UARJ), 1, 103-108.
- Dhenakaran, S.S. and Parvathavarthini, A. (2013) An Overview of Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 3, 251-259.
- .Ehsan, Z. Uzmi, “Performance comparison of adhoc wireless network routing protocols”, Proceedings of IEEE International Multi-topic Conference (INMIC) 2004
- Panda, I. (2012) A Survey on Routing Protocols of MANETs by Using Qos Metrics. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 2, 120-129.
- Abolhasan, M., Wysocki, T. and Dutkiewicz, E. (2004) A Review of Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 2, 1-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1570-8705(03)00043-X
CrossRef
- Mbarushimana, C. and Shahrabi, A. (2007) Comparative Study of Reactive and Proactive Routing Protocols Performance in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. 21st International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, AINAW’07, Niagara Falls, 21-23 May 2007, 679-684.
CrossRef
- BR, A.K., Reddy, L.C. and Hiremath, P.S. (2008) Performance Comparison of Wireless Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols. IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, 8, 337-343.
- Guo, J. and Wang, A. (2014) Study on Integration OLSR Protocol in Mobile Ad Hoc Network. Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Linear Drives for Industry Applications, 4, 701-708.
CrossRef
- Bali, S., Steuer, J. and Jobmann, K. (2008) Capacity of Ad Hoc Networks with Line Topology Based on UWB and WLAN Technologies. Wireless Telecommunications Symposium, Pomona, 24-26 April 2008, 17-24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/WTS.2008.4547538
CrossRef
- Lol, W.G. (2008) An Investigation of the Impact of Routing Protocols on MANETs Using Simulation Modelling. Auckland University of Technology, Auckland.
- Perkins, C.E. and Bhagwat, P. (1994) Highly Dynamic Destination-Sequenced Distance-Vector Routing (DSDV) for Mobile Computers. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 24, 234-244.
CrossRef
- Boukerche, A., Turgut, B., Aydin, N., Ahmad, M.Z., Bölöni, L. and Turgut, D. (2011) Routing Protocols in Ad Hoc Networks: A Survey. Computer Networks, 55, 3032-3080. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2011.05.010
CrossRef
- Bakht, H. (2011) Survey of Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Research, 1, 258-207.
- Royer, E.M. and Toh, C.K. (1999) A Review of Current Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks. IEEE Personal Communications, 6, 46-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/98.760423
CrossRef
- Wan, T., Kranakis, E. and Van Oorschot, P.C. (2004) Securing the Destination-Sequenced Distance Vector Routing Protocol (S-DSDV). In: Information and Communications Security, Springer, Berlin, 358-374.
CrossRef
- Dhenakaran, D.S. and Parvathavarthini, A. (2013) An Overview of Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 3, 251-259.
- Humblet, P.A. (1991) Another Adaptive Distributed Shortest Path Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 39, 995-1003. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/26.87189
CrossRef
- Rajagopalan, B. and Faiman, M. (1991) A Responsive Distributed Shortest-Path Routing Algorithm within Autonomous Systems. Journal of Internetworking: Research and Experience, 2, 51-69.
- Chowdhury, S. A., Uddin, M. A., and Al Noor, S. (2012) A Survey on Routing Protocols and Simulation Analysis of WRP, DSR and AODV in Wireless Sensor Networks.
Views: 18,602

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
![Figure 1. Types of Routing Protocols [2]](http://www.computerscijournal.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Vol10_No1_Com_Sac_Fig1-150x150.jpg)