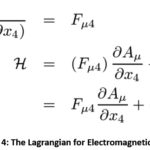Introduction
Every theory in the making is quite enchanting.9
Ignore everything that does not fit into the theory becomes an acceptable norm.
In the process, either fortunately or unfortunately, educating the young minds
invariably gets delayed. The Wright brothers observed the flight of birds to
make an aircraft.3 There is no evidence of plenty of data being
collected and simulations of birds in flight done by the Wright brothers. Yet,
the aircraft happened. It is a pity that educating the young minds to use such
methods got delayed both for right and wrong reasons.
Clayton Christensen coined the phrase
“Disruptive Technologies” in his 1997 book titled “The Innovator’s Dilemma: When
New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail”. Gradually the phrase “Disruptive
Innovation” came into regular use. It is all about passion and privation.
“Automation” always ranks very high in any list of disruptive technologies15
that have been influencing the world. Automation has the following facets:
Use
Voluntary activation or deactivation of
automation by human operators.
Misuse
Over reliance on automation
Disuse
Negligence or Underutilization of Automation
Abuse
Automation without due regard for the
consequences for the Human
The nature of technology is such that the users discover new ways of using it as they progress in deploying the technology. It is not uncommon for even naïve users to think of new applications which the developers have not thought of. Unintended Use of technology often implies a pronounced thrust to works an unforeseen use warranting improvements in the associated systems and sub-systems. In other words, there is a high chance of many hazards at various levels tormenting the stakeholders for a reasonable spell of time. Responsible innovation factors the standardization life-cycle as well. It is the grey area where the definitions and standards are yet to emerge that is a serious particularly when life forms are involved.
Cyborgs brought in a wide range of Electronic Implants.
A bio-electronic implant, which is about the size of a pencil eraser, would actually sit behind the retina at the back of the eyeball, and images would be transmitted to the brain via a connector the width of a human hair. One can see images better. This is just one case in point.
Material and Methods3,5
“The highly developed living being is an open
system having many relations to its surroundings – in the respiratory and
alimentary tracts and through surface receptors, neuromuscular organs and bony
levers. Changes in the surroundings excite reactions in this system, or affect
it directly, so that internal disturbances of the system are produced. Such
disturbances are normally kept within narrow limits, because automatic
adjustments within the system are brought into action, and thereby wide
oscillations are prevented and the internal conditions are held fairly
constant.”
–Walter B Cannon, “Organization for
physiological homeostasis”, Physiological Reviews, 9:399-431, 1929.
Engineers have developed machines that could
implement homeostatic behavior. The quest for making these machines emulate
human intelligence was natural. Rapid advances in miniaturization have fuelled
various processes of affordable body modifying devices and appliances proliferate
the consumer markets.4
“As a result of these comments (fluctuations
of magnetic fields of the earth may cause undesirable behavioral changes), I
was contacted by Dr. James Hamer of Northrop Space Laboratories, who informed
me that his group was already involved in this area. He also noted that Dr.
Norbert Weiner of MIT, the originator of cybernetics, had been interested in
the same subject.
Weiner had been involved in a German
experiment in which human volunteers were unknowingly exposed to a
low-intensity, 10-Hz electrical field. The subjects reported feelings of unease
and anxiety when the fields were turned on. Both Hamer and Weiner were working
under the assumption the ELF internal rhythms in the brain were determinants of
behavior, and that pulsing external fields could “drive” these
internal rhythms, thereby altering behavior.”
– Robert O Becker, “Crosscurrents”, Tarcher
Perigee, 1990
In theory a combination of body modification
and generation of impulses that can penetrate the Blood – Brain – Barrier more
easily than the presently known drug formulations and psychedelic substances
may result in a superior functioning of the human brain. A combination of
sophisticated drugs and technologies do hold the promise of making superhuman
and terrific creatures. This article is more about the impact of such practices
on the human brain.
“An intelligence that could at a given moment
comprehend all the forces by which nature is animated and the respective
situation of the beings who compose it, if it were sufficiently vast enough so
as to submit this data to analysis, would encompass in one single formula the
movements of the greatest bodies of the universe and those of the lightest
atom; for this intelligence, nothing would be uncertain and both the future, as
well the past, would be present before its eyes.”
– Pierre – Simon Laplace, “Essai
philosophique sur les probabilities”, 1814
The sign of life is a pulse. It is the beat
that all living systems answer to. It is perhaps the seed with which the energy
cascades, feedback cycles and the dynamics happen in accordance to a principle
of circularity that ensures maximum safety to the living systems. Pulse it is
that challenges the notion of path of least resistance in the design of circuits12
that work on electronic pulses. The present day technocracy has shifted the
societal thinking towards faith in machines and a narrow path of cause – and –
effect logic they are made up of. The foundation for such a view is usually
attributed to Rene Descartes who postulated that the world outside is just a
vast and intricate machine.
Computing brought with it the notion of a
“Clock” that controls the timing in the execution of a given sequence of
actions expressed in a lingua franca that is compatible with the machine on
which they are executed. Pulse which is the sign of life began to be modeled as
a combination of system clocks and the electronic pulses in the circuitry. In
reality a far superior model for pulse is mandatory. The world has its own best
model.1
The role of biology is the key because it
provides guiding principles and suggests useful components. A very important
lesson from biology is the scale of structural components. The lower energies
involved in non-covalent interactions make it much more convenient to work on
the nanometer scale (or lesser) utilizing the biological principle of
self-assembly.
There are two major technical issues. One is
positional control (holding and positioning molecular parts to facilitate
assembly of complex structures) and the other is self-replication. The vital
factor is the engagement with the outside world that brings into sharp focus
two difficult concepts termed as Intentionality and Free – Will. The challenge
of ensuring the preservation of the intent in making a given technology and
while giving a thrust to the exploratory nature of the free – will of the
consumers has no unique solution. This article outlines the inter-play of
Intentionality and Free – Will in the context of body Implants (Alexis, 1939).
Some
Lessons from Bio-Medical Instrumentation
The Bio-Medical Instrumentation2
which includes Recording and monitoring instruments, Measurement and analysis
techniques, Modern imaging systems and Therapeutic equipment has a
physiological basis. The physiological aspects of several internal organs is
modeled as an electric activity. It is useful to observe that a large
proportion of these activities captured as associated signals are presently not
deemed very useful in clinical practice are most of them elude precise
measurements. However, patient care has improved significantly due to the
signals that are of diagnostic significance. Electric conductivity in the human
body is presumed to be due to ions serving as charge carriers. Special electrodes
perform the necessary transducing function between the ionic solutions and the
electronic circuitry of the instrument. These electrodes are now highly
sophisticated and can be made for any organ of the human body. These electrodes
provide the bio-potential interfaces. To some extent the behavior of a given
organ can be influenced using therapeutic equipment that deploys such
interfaces. Clinical Medicine opines that the associated practices are for
healing some organs and may not be advisable to use these practices for
enhancing the performance of healthy organs.
Technologists however keep attempting to build
completely autonomous creatures that co-exist in the world of humans and are
perceived by the humans as intelligent enough in their own right.13
There are two major technological advances namely Robotics and Cyborgs that
remain in focus in the context of use of technology.
Robotics
and Cyborgs18
The history of robots has its origins in the
ancient world. Concepts of artificial servants and companions date at least as
far back as the ancient legends. In Greek mythology, Hephaestus created
utilitarian three-legged tables that could move about under their own power and
a bronze man, Talos, that defended Crete. The myth of Pygmalion whose statue of
Galatea came to life is very interesting. Around 1495 Leonardo da Vinci
sketched plans for a humanoid robot. The ancient Hebrews wrote about a person
made out of dirt and clay called a golem. The golem was created to help with
menial labor. The ancient Greek god Hephaestus was believed to build himself
mechanical assistants out of gold.
The Indian Lokapannatti tells the story of
King Ajatasatru of Magadha who gathered the Buddhas relics and hid them in an
underground stupa. The Buddhas relics
were protected by mechanical robots (bhuta vahana yantra), from the kingdom of
Roma Visayar; until they were disarmed by King Ashoka.
Scaling was the first of the Two New Sciences
revealed in Galileo’s Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations (1638);
physics was the second. Galileo observed that “…..a horse falling from a height
of three or four cubits will break his bones, while a dog falling from the same
height … will suffer no injury?..” The study of materials has thus been a
real challenge. “Robotics” is one discipline of research that blends certain
aspects like intelligence of the live forms with the materials as understood by
the physicists. “Big is weak, small is strong” is the result of this research.
Isaac Asimov gave the following Laws of Robotics:
A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm;
A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law
A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law
The Zeroth Law: A robot may not harm humanity, or, by inaction, allow humanity to come to harm.”
Many ideas related to Robots thus began to be
seen as dominated by Mechanical and Electrical Engineering. Today, it is now
possible to envisage human sized robots with the capacity for near human
thoughts and movement. Robots have thus become inter-disciplinary and computing
and related ideas began to find place in this very important area.
Very soon miniature robots were on the anvil.
Today, we have excellent fabrication technologies and we made rapid progress in
Nanorobotics that are playing an important role in diagnostics and drug
administration within the human body.
“Cyborg” is an innovation to enhance the
capabilities of the human being in some manner. The term “cyborg” is used to
refer to a man or woman with bionic, or robotic, implants. There are two
popular methods of making a Cyborg. One method is to integrate technology into
organic matter resulting in robot-human. The other method is to integrate
organic matter into technology resulting in human-robot. Cyborgs were well
known in science fiction much before they became feasible in the real world.
Cyborgs are being experimented with in Border Crossings, Engineering the Body
Electric, Machinic adventures in Space, Prosthetics, Spiritual Cyborgs, Mind
Uploading and such challenging ideas. The Ethics of Cyborgs is a very important
area of research. There have been a good number of indicators for involuntarily
implantation into humans.
Why
do Consumers want Implants?
It is a matter of inconvenience to pull out an
Identification Card to make the RFID sensors take cognition of the Individual.
It would be nice if that is done by a miniature implant of the RFID card under
the skin and this process is fully automated. In a sense, the physical body
becomes machine readable and has many ramifications in the way Smart Cities
happen all over the globe.
This is a simple use of implants that is very
realistic. Human organ Performance enhancement implants are increasingly in
demand.11 The potential risks to health associated with such
implants are: adverse tissue reaction, migration of implanted transponder,
compromised information security, failure of technology at various stages
including an overhead high tension electrical cable inducing deathly currents
through the implants or camera flash lights, electromagnetic interference,
electrical hazards, incompatibility with imaging technologies, and possible
needle stick injuries.
This is true even if the positivism associated
with faith in humanity at large prevails on such unintended uses of technology.15
The
Quagmire of Networking
Smart sensors are being used to improve
agriculture from farming lettuce to producing beef and even protecting bees.
From smart pans to connected scales, the internet of things is now tackling the
art of cooking. Connected Cars, Consumer Electronic goods that provide
Integrated Services are now regularly used.7 The connected world is
transforming markets with affordable, multi-purpose smart devices.
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an
approach to building computer networking equipment and software that separates
and abstracts elements of these systems. SDN decouples the system that makes
decisions about where traffic is sent (the control plane) from the underlying
system that forwards traffic to the selected destination (the data plane). The
Open Networking Foundation was founded to promote SDN standards and engineering
as Cloud Computing blurs the boundaries between networks and computers. Implant
within the Human Body is just another abstract element in the SDN.
Technology Assurance addresses the following
three main challenges:
Trustworthiness
No exploitable vulnerabilities exist, either
maliciously or unintentionally inserted
Predictable
Execution
Justifiable confidence that technology
functions as intended
Conformance
Planned and systematic set of
multi-disciplinary activities that ensure processes and products confirm to
requirements, standards/ procedures.
Sustainable technologies indeed help us build
a positive for generations to come. However, they are often deployed to weather
the storms of short-term exigencies, disruptions and disasters. Long-term societal conditions warrant a
switch back to self-reliance when technology fails. This is becoming
increasingly difficult in societies that have taken to the technocracy path of
addressing the complex demands of the global villages.
“The older people used to say that the trees,
the rocks, the birds, and the animals used to talk. They had a voice, and
today, as I realize it, they still have a voice. My People always say that you
have to take care of them in order for you to continue on. If you don’t, when
they die off, you are going to die off with them.”
–
Corbin Harney, spiritual leader of the Western Shoshone Nation, from The Way It
Is
The
Reality Check from Medicine6, 16
Implants can potentially result in14:
Alzheimer’s disease
Delusional
Schizophrenia
Electrical currents running into and/or through various body parts
Electrical shocks to various body parts
Electrical jolts to random body parts
Deep pain/aches various body parts
Burning sensations to various body parts (often internally),
Pressure in the head and various body parts
Clicking/popping sounds in the head
Heart problems
Palpitations
Major organ failure
Various cancers
Involuntary body movements
Forced speech
Slow memory recall
Erased memory of set periods of time or timed dementia
Continuous headaches that are near impossible to heal
Ear aches
Ear hums and clicks
Piercing high pitch sound inside ears
Multiple Chemical Sensitivity / Electro-sensitivity
Sudden unconsciousness
Mimicked voices/conversations to the head – But no one is there – (Known as the auditory effect)
It is very easy for a trusted professional to
embed an implant into the human body (or any living being) without informed
consent through an open wound during a surgery or use of an intravenous needle
including dentistry needles and in the form of pills form. X-Rays and other
scans seem to be doctored or remain untraceable for regular checks. Many suffer
in silence due to the possible undetected and unintended or abuse of a very
sophisticated technology.
Results
and Discussion17
Measuring body temperature is very important
in medicine. Change in body temperature is vital to the functioning of any
implant used for body modifications mooted in this paper. Temperature
regulation is a type of homeostasis, which is a process that biological systems
use to preserve a stable internal state to survive.
In physics and mathematics, the heat equation is a partial
differential equation that describes how the distribution of some quantity
(such as heat) evolves over time in a solid medium, as it spontaneously flows
from places where it is higher towards places where it is lower. It is a
special case of the diffusion equation that governs the process by which
molecules spread from areas of high concentration to areas of low
concentration.. This equation was first developed and solved by Joseph Fourier
in 1822 to describe heat flow. It is of fundamental importance in diverse
scientific fields. It is vital for Electronics and Communications.
The general heat conduction equation is given
in the Figure 1 below.
Classical Physics is based on the solution for these equations.
The difference between quantum physics and classical physics is that classical
physics only works within a certain range of phenomena. Typically, when one
starts talking about things that go on at the level of photons and electrons
classical physics no longer gives reliable answers. It is no longer a
“useful fiction”.
The Theory of Relativity requires that the laws of nature are
invariant to the reference frame. This is not satisfied by the Newtonian
formulation of mechanics which assumes one absolute frame of reference and a
separation between space and time. In contrast, the Lagrangian and Hamiltonian
formulations of the principle of least action remain valid in the Theory of
Relativity once the Lagrangian is written in an invariant form.
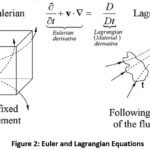
The calculus of variations is concerned with the maxima or minima [collectively called extrema] of functionals. In simpler terms, a function showing the shortest path following all the known rules of the system is called the Lagrangian. In physics, it is typically the least amount of action that is the desired Lagrangian.
A strong extremum is also a weak extremum, but the converse may
not hold. An example of a necessary condition that is used for finding weak extrema
is the Euler–Lagrange equation seen in Figure 2.
Spotting the “extremum” points is easy and is governed by geometry of abstract spaces and / or “Sacred Geometry”. The core challenges are Inclusion and Interaction.8
“Geometry” literally translates from Greek as “land
measurement”, and reflected a popular Greek belief that they learned it
from Egyptian “rope stretchers”, land meausurers, who used ropes to
perform what came to be called straightedge and compass constructions. The
Human Form can perhaps be abstracted as “Sacred Geometry” for the
dynamics it can possibly mirror in the cosmos.
Sacred geometry, or spiritual geometry, is the belief that numbers
and patterns such as the divine ratio have sacred significance. Concepts of
sacred geometry are expressed in the beliefs of Christians, Jews, Hindus,
Muslims, and other formal religions. Pythagoras taught that each number had its
own peculiar character, virtues, and properties. Everywhere in this cosmos, the
Circle, Triangle, Square, Hexagon, and so on remain the same unchanging
archetypes.
This paper proposes the nanotechnology that
reflects the human form as a progress of Geometry from Earth into the Cosmic
Spaces. Such a nanotechnology reflects the geometry of any given human form
even with body modifications in an abstract space that indicates the
modification and the associated intentionality and free-will. Please see Figure
3 and Figure 4.
Towards
a Better Comprehension of Human Body14
Technology thrives on a language that weaves
brilliant sequences of calculations, hypotheses and positions reality in a
framework of unutterable abstractions (Henry, 2013). Biological sciences are
founded in an inextricable jungle that is not amenable for definition using algebraic
equations.10
(Late) Sir John Maddox, the well-known former
Editor-in-Chief of Nature wrote an article titled “The Unexpected Science to Come…”
while ushering in the year 2000. This article by (Late) Sir John Maddox was
published in the December 1999 issue of the Scientific American.
“The most important discoveries of the next 50
years are likely to be ones of which we cannot now even conceive” is the advice
that is indeed apt at the stroke of the year 2000. (Late) Sir John Maddox goes
onto add that “Our understanding of the human brain is incomplete in one
conspicuous way: nobody understands how decisions are made or how imagination
is set free”.
In fact, the quest to understand the human brain got into the realms of Computer Science several decades back. Not entirely unrelated are the following set of really big questions one must answer to hopefully replicate the activities of human brain using technology in some form.
What is Intelligence?
What is life about?
What is Thought?
How did Language Evolve?
What is Consciousness?
Does GOD exist?
Human body cannot be separated into parts that
are isolated from one another, modeled as objects or things that have only
known relationships. Through the senses of fellow human beings and the
sophisticated scientific instruments the dynamics within a human body appear to
be physical, chemical, physiological, or psychological. A possible science
demands the use of practically every other science. The sheer complexity of
such an inter-disciplinary science is daunting.
Conclusion
The technology has advanced considerably over
the past few years. Support systems that include the practice of medicine have
been simplified. However, detection and repair systems outside of the human is
very likely to take a longer time. It is wise to educate the consumers11
on the indicated unintended and abuse of advanced technologies that are very
enticing and enchanting. There are many hazardous presumptions and assumptions
that are hard to revisit at a later time. The biological sub-systems in the
process would have been impacted in an irreversible manner very soon. Taking
recourse to the mathematical foundations of geometry and morphogeneis is
presently the most optimal method of safe and secure decoding of this usage of
highly advanced technologies.
Acknowledgements
The author thanks
Anna University, Chennai, the Steering and Program Committees of the “Theory
and Applications of Models of Computation [TAMC]” series of conferences and the
various committees of 21st Century Norbert Wiener [21CW] series of
conferences for the opportunitites and support to work on this research.
Funding
There is no
specific funding source for this research outside of the regular support
indicated in the Acknowledgement.
Conflict of Interest
This is a
single author paper. There is no conflict of interest.
References
- Alexis Carrel (1939), “Man, The Unknown”, Harper & Brothers, USA.
- Arumugam M (2014), “Biomedical Instrumentation”, Anuradha Publications, Chennai.
- Daniel C. Dennett (1988),“Evolution, Error and Intentionality”, Y. Wilks and D. Partridge, [Eds], Sourcebook on the Foundations of Artificial Intelligence, New Mexico University Press, USA.
- Chris Woodford (2015), “Atoms Under the Floorboards”, Bloomsbury Sigma, New York, USA.
- Dale Jacquette (2014)., “Art, Expression, Perception and Intentionality”, Journal of Aesthetics and Phenomenology, Vol. 1, No. 1, Pp 63-90.
CrossRef - Franssen Maarten, Kroes Peter, Vermaas Pieter, Light Andrew and Moore Steven. (2008), “Design, Use, and the Physical and Intentional Aspects of Technical Artifacts”, n Book: Philosophy and Design – From Engineering to Architecture,Springer.
- Gopal T V (2016), “Engineering Software Behavior in Cyber – Physical Systems”, International Journal of Engineering Issues, Vol. 2016, no. 1, pp. 44-52.
- Gopal T V (2019), “Geometric Simplification of Cyber-Physical Systems”, Maya Dimitrova and Hiroaki Wagatsuma [Eds], “Cyber-Physical Systems for Social Applications” (Pp 222 – 239), IGI Global USA.
CrossRef - Henry Smith Williams (2013), “The Beginnings of Science”, Apple Publishing International (P) Ltd., India.
- Matthew Stein (2000),”When Technology Fails – A Manual for Self-Reliance & Planetary Survival”, Clear Light Publishers, New Mexico, USA.
- Melissa Leach, Ian Scoones and Brian Wynne (Editors) (2017), “Science and Citizens”, Orient Longman Pvt. Ltd., India.
- Neuman, M. R. “Biopotential Electrodes.” The Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second Edition. Ed. Joseph D. Bronzino, Boca Raton, CRC Press LLC, 2000.
CrossRef - Paul Bloom (1996), “Intention, History, and Artifact Concept”, Cognition, Volume 60, Issue 1, Pp 1-29.
CrossRef - Robert Frenay (2006), “Pulse – How Nature is Inspiring the Technology of 21st Century”, Little Brown Book Group, UK.
- Samuel Florman (1982), “Blaming Technology: The Irrational Search for Scapegoats”, St Martins Pr, USA.
- Sipi Helena(2003), “Artefacts and Living Artefacts”, Environmental Values, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 413–430.
CrossRef - Suresh Ganzi, Kavuluru Lakshmi and Mantrala Mallik. (2017). “A Review on Development of Medical Implants by Rapid Prototyping Technology”, International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Vol 117, No. 21, Pp 257-276.
- Verbeek Peter-Paul (2008), “Cyborg Intentionality: Rethinking the Phenomenology of Human-Technology Relations”, Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 7, Pp 387-395
CrossRef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.