M. Kamalakannan* , K. Devadharshini
, K. Devadharshini
College of Fisheries Engineering, Tamil Nadu Dr. J. Jayalalithaa Fisheries University, Nagapattinam, 611002 India.
Corresponding Author E-mail: mkkannan704@gmail.com
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojcst12.02.05
Article Publishing History
Article Received on : 25 May 2019
Article Accepted on : 2 July 2019
Article Published : 02 Jul 2019
Plagiarism Check: Yes
Article Metrics
ABSTRACT:
In food processing industry, there arises a need to control a conveyor belt. currently industries are very necessary to use material handling system for to move materials from one place to another place continuously and to minimize operations time. Stepper Motor is suitable for controlling conveyor because of its high accuracy positioning over a short distance and provide high torque even at low speeds and it is also offer very low vibration and a wide range of features. This paper is focused on controlling the speed of the conveyor belt through the speed of stepper motor using the micro processor namely, Raspberry Pi 3B+’s (RP 3B+) GPIOs (General Purpose Input Output) and it can be generate sequence of control signals on the GPIO pins of RP 3B+. Interfacing the stepper motor with RP 3B+ using python programming language. The method is explained with the results of changing the weights the speed level is reduced through time variation on the conveyor belt and the model of working Conveyor belt with Stepper motor controlled by python and RP 3B+ with Easy Driver(A3967).
KEYWORDS:
Conveyor Belt; Python; Raspberry pi 3B+; Stepper Motor
Copy the following to cite this article:
Kamalakannan M, Devadharshini K. Controlling the Speed of Conveyor Belt using Python – Raspberry Pi 3B+. Orient.J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;12(2).
|
Copy the following to cite this URL:
Kamalakannan M, Devadharshini K. Controlling the Speed of Conveyor Belt using Python – Raspberry Pi 3B+. Orient.J. Comp. Sci. and Technol;12(2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2xsbzag
|
Introduction
In the world of food processing industry, there are still a few
areas in which it is quite sufficient to transport manually from one place to
another place of the material components, but, for high-unit loads, automated systems
have become essential part of it. Conveyors
are durable and reliable components used in
automated distribution and warehousing, as well as manufacturing and
production facilities. In combination with computer-controlled pallet handling
equipments, it allows for more efficient retail, wholesale, and
manufacturing distribution. It is considered a labor saving system that
allows large volumes to move rapidly through a process and allowing industries
to ship or receive higher volumes with smaller storage space and with
less labor expense. With this in
mind, Henry Ford deployed belt conveyors for mass production (Wilson, 1996). Priyanka
et al., (2019)proposed the system of detecting and automatically sorting the
parcels with QR code using QR code scanner on the conveyor belt using micro
controller Arduino. Rahul et al.,
(2018)presents the sorting of
objects using Computer Vision techniques with a conveyor belt, stepper, servo motors
and mechanical structures.
Ajinkya et al., (2017)
illustrated the system of automatic human queue management at public places
using conveyor belt with stepper motor and micro controller. It placed two
conveyor belt one at the site window and other at the entry window and boom bar
as separator to avoid crashes among the people which is controlled by the micro
controller. Likewise, it placed the stepper motor to control the conveyor belt
for proper direction. Chavhan and Rode (2018)introduced the system to detect the quality of the fruit using
raspberry pi with Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) for background removal
and Support Vector Machine (SVM) for classification of colour on the conveyor. Akshay
et al., (2017) explained the concept
of sorting and counting of the object and displayed its quantity by using
digital Image Processing, objects were detected and sorted which were passing
over conveyor using a micro controller. Jyothi and Harsha (2017)developed
the control system to separate different objects with different specification
and to locate them in different locations. The product information can be sent
immediately and accurately without any wireless to the monitor. It is a
valuable method for wireless communication achieving accuracy in data
transferring and receiving.
Sheela et al., (2016) presents
the sorting of the objects on a conveyor belt depend on its size and colour by
using sensors, raspberry pi 3 and linear actuators. It used the low cost
automated system with Raspberry pi along with USB camera is to detect of the
colour of the object by using python and openCV. If the object is desired
colour, it will be carried on the conveyor belt and it will be received at the
end of the conveyor belt into the trolley. If it is not the desired colour, it
will activate the actuator. Then, the linear actuator will throw away the
object into another trolley and the conveyor belt run with another object for
the desired colour. Shreeya et al.,
(2016)developedthe design of box sorting machine and used the pneumatic actuation
to sort the boxes automatically to reduce cost and time. Automation process
read the barcode from the cover of box with the help of camera of the raspberry
pi. Raspberry pi decoded the barcode which sorted the boxes and also gives
signal to motor driver to stop and start motor accordingly.
Sanjay and Rohan (2015)designed
the automated sorting machine using
conveyor belt. It is mainly to avoid the size malfunctioning in production
industry. It has the ability to sort the object of different sizes so it is
called as the intelligent conveyor belt. Different size objects are passed
through the sensors and the specific size object is sorted. The controller is controlled
by the circuit which drives the belt. This system will also help to
segregate heavy and bulk objects. Karthik
Kumar and Kayalvizhi (2015)presents
the real time application for object, colour, shape and size detection on the
conveyor belt. OpenCV is used at real time is used to determine the colour of
the object placed over a moving conveyor belt. While passing over a conveyor
belt serially, this system will differentiate various different types of
packages at the real time. Manasa et al., (2015)developed and implemented the object counting algorithm based on
real time by using Raspberry pi with image processing.
From the above literature is based on controlling the conveyor belt
with many other drivers and micro controller. But, A3967 easy drive with RP 3B+,
no one is tried to control the speed of conveyor belt using a stepper motor and
interfacing with python language. This paper is focused on controlling speed of
conveyor belt connects with 12v bipolar stepper motor then it is controlled by
the Raspberry PI 3B+ along with easy drive (A3967).
Material and Methods
The following materials (including Hardware and Software) are used
to controlling the speed of converyor belt
Raspberry pi 3B+
Raspberry Pi was developed in
February 2012 in UK by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote basic computer
science education in schools and colleges. The original model is becoming much
more popular than expected and is selling for robotics outside its market.
There are no peripherals and cases (e.g. mice and the keyboards). However,
certain accessories were included in several official and unofficial bundles.
The Raspberry Pi Foundation has developed the first two models. After releasing
the Pi model B, the Raspberry Pi Trading Foundation set up a third model, B+
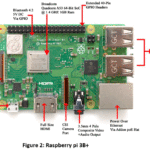
and the logo is shown in Figure 1.
Models In Raspberry Pi: (1). Model A; (2). Model A+; (3). Model B; (4).Model B+.
Specifications
Model B+ of the Raspberry Pi
3 is the newest Raspberry Pi of single computer board. Developed from the
previous Raspberry Pi 3 Model B, it offers enhanced speed and performance. RP
3B+ is more faster than previous models and the features is Broadcom BCM2837 Processor, Quad core ARM
Cortex-A53, 64 bit CPU cor, 1.2GHz (Roughly 50% faster than Pi2) Clock speed,
400 MHz video core IV® GPU, Ethernet (RJ45 Port) Network connectivity, 802.11n
wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) and Bluetooth 4.1, four USB 2.0 ports,40 Pin Header of
GPIOs, 15-pin MIPI Camera interface, DSI 15 Pin/ HDMI Out/ Composite RCA
Display interface, 2.4 APower supply alongwith Raspbian operating system
(similar to linux operating system) is shown in Figure 2. There are many
advantages of RP 3B+: Trouble shooting tool, Efficient energy, Cheap to
purchase, Easy operation and connectivity, Low energy consumption, No need of
external energy and Easily access to any applications
12v Bipolar Stepper motor
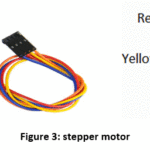
Figure 3 shows the model of stepper motor, and it is a type of
control motor which can be used to control speed and positioning without using
a feedback loop, which is the so-called open-loop motor control. Bipolar stepper motors there is only a single
winding per phase. The driving circuit needs to be more complicated to reverse
the magnetic pole, it is done to reverse the bipolar stepper motor – circuit
specialists blogcurrent in the winding. it is done with a H-bridge arrangement,
however there are several driver chips that can be purchased to make this a
more simple task. Because windings are
better utilized, they are more powerful than a unipolar motor of the same
weight. This is due to the physical space occupied by the windings. A unipolar
motor has twice the amount of wire in the same space, but only half used at any
point in time, hence is 50% efficient (or approximately 70% of the torque
output available). Though bipolar is more complicated to drive, the plenty of
driver chip means it is much less difficult to achieve. An advantages of 12v bipolar Stepper Motors is high accuracy
positioning over a short distance and provide high torque even at low speeds.
Stepper motors also offer very low vibration and a wide range of features. The motor’s life depends therefore on the
shaft bearing’s life. Good choice for high-precision low-speed applications. It
has Low-speed Synchronous Rotation.
Angle of the rotation is proportional to the input pulse.
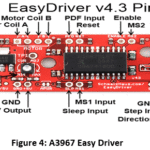
A3967 Easy Driver Circuit
It is a complete micro stepping
motor driver for easy operation built with translator and minimal control
lines. Its design is basically to operate bipolar stepper motors in full, half,
quarter and eighth-step modes. Figure 4 shows the A3967 easy driver and it is easy-to-use
stepper motor driver, compatible with anything capable of delivering a digital
0 to 5V pulse. It requires a power supply between 6V and 30V for the motor and
can power supply for any stepper motor in this voltage. A digital interface
voltage control unit can be set to 5V or 3.3V on the Easy driver. Connect a
4-wire stepper motor and a microcontroller with precise motor control. An advantages
of this driver is made up of Fibre class material and no battery
required to operate this easy driver, also can provide any external power
voltage up to 30v.
Conveyor Belt
Basically it is very wide belts attached in a
loop to two or more turning rotors driven by stepper motors and it is an endless belt moving over two end pulleys of a length of belt
either by vulcanized splicing or by using mechanical fasteners at fixed positions. It is mainly used for transporting material
horizontally or at an incline up or down. The loop is the actual conveyor belt, and is generally made of two or
more layers of rubber, one layer to give shape and structure to the belt and
one to allow it to transport its load safely. This conveyor loop is generally
attached to two wheels, called rotors, which are spun by stepper motors.
The extra length is to make the belt endless to
required size can be calculated by the following formula:
Splice Length = W + 150 (N-2) + 25mm (1)
where, W is width of belt (in mm), N is the
number of plies.
Calculation of Belt Roll Diameters (meters)
D = 4d.L / ρ + K2
(2)
Where D = Roll Diameter (m); d = Belt Thickness (m); L = Belt Length
(m);K = Diameter of Core (m);
=Density of Belt (kg/m³).
Table1: The details of major
components
|
Belt
|
Tractive element used for moving and supporting
|
|
Pulley
|
To move the belt and control its tension
|
|
Drive
|
Impart power to the pulley to move the belt and its
load
|
|
Structure
| Support and maintain the alignment of the pulley, idlers and driving machinery |
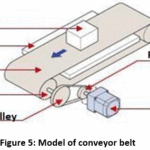
The conveyor belt has enough friction between it and the rotor that it sticks to this rotor. As a rotor turns, the conveyor belt will turn as well due to the intense friction between the rotor wheel and the belt. This turning motion of the rotor causes one side of the belt to move in one direction, while the other moves in the opposite direction. This means that both wheels must always be moving in relatively the same direction, either clockwise or counter-clockwise. Application of conveyor belt is to convey products or raw materials through the use of either friction or mounts on the belt meant to hold the product in place as the belt moves. Figure 5 show the model of conveyor belt and Table 1 gives the details of major components of conveyor belt.
Controlling speed of stepper
motor and conveyor belt
The hardware materials (given in above) and softwares are mainly
used for controlling the speed of conveyor belt. The details of software were discussed below.
Python
Since 1991, Guido van Rossum developed the hign level programming
language is known as Python. The benefits of using Python codes over other
language codes for object detection are more compact and readable code. It is
free and open source and has a multiple functions that can be packaged in one
module. This compact modularity has made it particularly popular as a means of
adding programmable interfaces to existing applications.
Figure 6 describes the pseudo code of python programming language
for interfacing 12v bipolar stepper motor and RP 3B+. From this programme, the speed, number of
steps and direction of stepper motor is fully controlled by RP 3B+. Two GPIO
pins of RP 3B+ are used and connected with A3967 easy driver, one is for number of steps and another one is
direction for stepper motor. If the
spinmotor command of direction is true the stepper motor is rotating clock-wise
otherwise the motor is rotating counter-clockwise. If reducing the values of
time sleep the speed of stepper motor is increase.
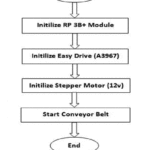
Figure 7 illustrates that the flow chart for controlling speed of conveyor belt. Initially A3967 easy driver with connected RP 3B+ module GPIOs (General Purpose Input Output) and it can be generate sequence of control signals on the GPIO pins of RP 3B+. Then the control signals are passing from this easy driver to 12v bipolar stepper motor. Based on the control signals the conveyor belt is rotated continuously along with the stepper motor.
Results and Discussion
The hard connects with 12v bipolar stepper motor then it is
controlled by the RP 3B+ along with easy drive (A3967). As per instruction of
python coding the stepper motor is running at the allocated speed and rotation.
Figure 8
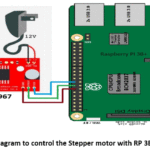
shows that the
circuit diagram to control the Stepper motor with RP 3B+, Easy Driver(A3967). GPIO pins 14, 16 and 18 of RP 3B+ are connected with ground,
steps and direction pins of A3967 easy driver respectively. In this work, 12v
bipolar stepper motor (4-wire) are to be used for the conveyor belt. Upto 5v stepper motor can get the power
signals from the RP 3B+ itself because, Rp 3B+ used to get from 5v micro USB
power supply. In this case, 12v bipolar
stepper motor are used and can get the power signals from the external 12v DC power
charger.
Figure 9 explained the model
of working Conveyor belt with 5v Stepper motor controlled by RP 3B+ with Easy
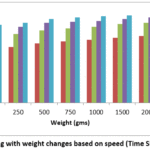
Driver(A3967). Figure 10 illustrates
the time varying with weight changes based on various speed (Time Sleep) level
of conveyor belt. It shows that the
changing of weights as per the speed level and it is reduced through time
variation on the conveyor belt.
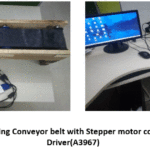 |
Figure 9: The model of working Conveyor belt with Stepper motor controlled by RP 3B+ with Easy Driver(A3967)
Click here to View figure
|
The multiple regression analysis is a statistical analysis for
estimating the relationship between various weights (y) in kilograms and time (x1,
x2, x3 & x4) for the data shown in the
Figure 10.
y = -2038.964182 x1 +
3204.259439 x2 + 6103.581801 x3 – 4785.575992 x4 –
9900.169409 (3)
where, x1,
x2, x3 & x4 are the values of
corresponding time sleeps with Residual Sum of Squares: RSS = 125986.2052; Coefficient of
Determination: R2 =
9.553127217·10-1
Conclusion
In this paper, a brief description of hardware materials (like, RP 3B+, Stepper Motor, A3967 Easy Drive) is presented to construct the converyor belt. The controlling Stepper Motor is described through an illustration for a python pseudo code. The circuit diagram and working model is presented to control the Stepper motor with RP 3B+, Easy Driver. The working model is explained for Conveyor belt with Stepper motor controlled by python and RP 3B+ with Easy Driver(A3967) The working method is explained with the results of changing the weights the speed (Time Sleep) level is reduced through time variation on the conveyor belt.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the anonymous reviewers whose comments have greatly improved this manuscript
Conflict of Interest
No.
Reference
- Ajinkya Kale, Shivani Naidu, Bhagyashree Patel, Poonam Khobre, Sunil Rathod. An Automated Human Queue Management Using Conveyor Belt, Sensors and Controller at Public Places, Holy Places or Shrines, International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)., 2017; 5(11): 2616-2620.
CrossRef - Akshay Varpe, Snehal Marne, Manasi Morye, Manisha Jadhav. Automatic Detection and Sorting of Products, International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and Technology., 2017:45-48.
- Chavhan P. R, Rode S.V. Colour based Quality Analysis of Fruits for Automatic Grading using Raspberry PI, International Journal of Innovative Research in Electrical, Electronics, Instrumentation and Control Engineering., 2018; 6(3): 6-8.
- Geda.Karthik Kumar, Kayalvizhi S. Real Time Industrial Colour Shape And Size Detection System Using Single Board, International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR)., 2015; 4(3): 529-533.
- Jyothi H. S, Harsha B. K. Design a Conveyor Based on Size and Color Separation of Product using Arduino UNO Microcontroller and Wireless Monitoring on Labview, International Journal Of Creative Research Thoughts (Ijcrt)., 2017; 5 (4): 2532-2539.
- Manasa J, Pramod J.T, Jilani S.A.K, Javeed Hussain S. Real Time Object Counting using Raspberry pi, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering., 2015; 4(7): 540-544.
- Priyanka A. P, Shreya Bhattad, Abhilasha P. S, Nilam Londhe, Siddharth Vhanmarathe, Pradeep Khot. A Work Paper on Automatic Parcel Sorting and Delivery to Section, International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET)., 2019; 7(4):1021-1023.
- Rahul Vijay Soans, Pradyumna G.R, Yohei Fukumizu. Object Sorting using Image Processing, 3rd IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT)., 2018.
- Sanjay Prakash Dabade, Rohan Prakash Chumble. Automatic Sorting Machine Using Conveyor Belt, International Journal of Innovative and Emerging Research in Engineering., 2015; 2(5): 66-70.
- Sheela S, Shivaram K. R, Meghashree S, Monica L, Prathima A, Shriya M.K. Low Cost Automation for Sorting of Objects on Conveyor Belt, International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology., 2016; 5(10): 195-200.
- Shreeya V. K, Swati R. B, Priyanka P. B, Firame G.B. Automatic Box Sorting Machine, International Journal for Scientific Research & Development., 2016; 4 (4):57-58.
- Wilson, J. M. Henry Ford: A Just-in-Time Pioneer. Production & Inventory Management Journal., 1996; 36(2): 26-31.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
 , K. Devadharshini
, K. Devadharshini